ADHD is the term used to describe inattentive, easily distractible, and impulsive individuals. It is a ‘neurological syndrome,’ not a disease. Many different factors are responsible for this disorder.
Initially, the term coined for it was hyperactivity and then attention deficit disorder. However, to differentiate between children who had ADD but did not exhibit symptoms of hyperactivity, the new term ADHD came into practice.
It can’t be prevented or cured. But recognizing it early and having a good treatment and education plan can help individuals manage their symptoms.
I have covered all the vital details you need to know about it; ADHD definition, its symptoms, diagnosis, self-treatment, and other essential factors to be considered.
Table of Contents
What Is ADHD?

ADHD stands for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. It is frequently used to describe people who have three main kinds of problems:
• Hyperactivity
• Impulsive behavior
• Inattentiveness
It is the most common ongoing psychiatric disorder of childhood. It is about two to three times more prevalent in boys than in girls.
Besides, it very frequently persists into adolescence and adulthood. And, if not treated timely, it may continue into adulthood, leading to severe problems during the adult years.
The disorder is likely to be transmitted by genes. Exactly how it takes place is not known, but it may be because of a difference in the chemical functioning in the brain.
Also, it often occurs with other disorders. The most common among them are learning disorders and behavioral disorders, such as ODD and conduct disorder.
So, first, begin with learning in detail the “Big Three of ADHD.” The types of ADHD include:
Inattention
Inattentive ADHD involves limited attention span, forgetfulness, or procrastination. People with this sub-type make careless mistakes because they have difficulty sustaining focus, following instructions, and organizing activities.
They are easily distracted by the external environment. Besides, they may leave tasks unfinished and appear not to listen to others. These are all symptoms of Inattentive type, not a personal defect.

Children with Inattentive sub-type may be preoccupied with their fantasy world. It is often misunderstood as laziness or apathy.
According to the NIMH, these symptoms are less likely to be recognized by parents, teachers, and medical professionals, and they don’t get timely treatment. It leads to academic frustration and guilt that can last a lifetime.
Workaholism, single-mindedness, procrastination are some common problems encountered in inattentiveness.
The Workaholic might have little difficulty sustaining focus but have great difficulty shifting it. Because of the inability to move attention between tasks, they can become engrossed in their job and forget everything else in the life.
We can see such similar behavior in the person with inattentiveness. He struggles hard to avoid distractions because of which he gets locked into his work that continues long until completed.
The Procrastinators have the opposite problem. They can’t selectively focus their attention and might be seen as lazy. But they are distracted by the outside world.
It makes it difficult to decide where or how to get started with the work. The thoughts keep on wandering, which prevents them from focusing on work.
Some common signs to recognize Inattentive ADHD:
- The children may miss questions they knows the answers to or skip whole sections in a hurry.
- ADHD in adults may be seen as failure to carefully proofread the work or email at the job, leading to unwanted embarrassment.
- Unfinished work, half-done projects, and incomplete assignments are all signs of attention problems in students. They don’t do it deliberately and may not necessarily disobey instructions.
- Difficulty in focusing during meetings, and completing projects on time, could be a sign.
- Students with inattentive type face a tough time focusing attention on instructions. Besides, their notebooks include more doodles than notes.
- Adults face social difficulty with people around at parties or gatherings. They tend to interrupt others in between and leave conversations about halfway.
- One of the most common indicators for this sub-type is distractability. They may miss an essential part of the story that someone is narrating and start their own story in between. But, it is crucial to know that distractability does not need to be present every time to detect inattentive sub-type in an individual.
- Also, they have difficulty organizing things. You will find their room disorganized and messy.
- Other people may see you as lazy, but unfortunately, these symptoms make you look lazy or careless.
- Another sign is forgetfulness. It includes forgetting things, names, and important dates.
According to DSM, at least five symptoms must be present to recognize it as an Inattentive sub-type.
- Difficulty in attending to details or makes careless mistakes during activities.
- They cannot sustain attention in tasks or play activities.
- Do not listen when someone is speaking to them.
- Does not follow instructions and fails to finish schoolwork or duties in the workplace
- Disorganized; difficulty managing sequential tasks and keeping things in order, and has poor time management skills.
- Tough time in sustaining mental effort on tasks.
- Loses things required for tasks or activities.
- Easily distracted by extraneous stimuli.
- Forgets daily activities like paying bills or attending meetings.
Hyperactivity
Many children with ADHD have been highly active since their early years. The most valid explanation of hyperactivity in children can be summed up as: always in motion, driven by a motor, constantly fidgeting, and shuffling their feet.
These individuals have a hard time sitting at a place for long and are disruptive. Children with hyperactivity often get up and walk around the class and bother other classmates.
However, it might be the first symptom to disappear as the child grows older. But, the adolescent or adult may continue to fidget or tap feet, be restless, and prefer energetic activities.
So, even if hyperactivity gets treated, other symptoms may not subside then too.
Common signs to recognize Hyperactive ADHD
- An adult may keep shifting his position or fidgeting with papers during meetings.
- The child may fall out of their chair more often than other classmates.
- Running around, crashing into furniture, or climbing on things can be some indicators of this sub-type.
- They can not sit quietly for long. And are often singing or humming. Besides, these people are very talkative. Known to be as a “motor mouth.”
- People irrespective of age may talk non-stop, interrupt others, and may struggle with self-control.
- They face difficulty in paying attention and doing quiet tasks.
Impulsivity
It is also one of the common characteristics of ADHD. Children of this type have poor impulse control. They can’t wait for their turns, and they need immediate gratification.
They become upset when things or people fail to behave as they want them to. It is also visible in poor planning and judgment, which is likely to be less age-appropriate.
Another prevalent symptom of impulsivity is difficulty in bladder control. Bed-wetting, which occurs in about 10 percent of all six-year-old boys, is three times more in these children.
Some common signs to recognize Impulsivity ADHD:
- They are highly accident-prone. As a result, these individuals receive more cuts, bruises, and wounds.
- They are disorderly and disorganized. It is entirely visible through the untidy rooms, untucked shirts, and careless reading and writing.
- Antisocial behavior might also be present in such children. They tend to steal and lie to their parents and teachers.
- The children find it hard to carry out activities that involve waiting.
- They are easily distracted by irrelevant things.
According to DSM, at least five symptoms must be present to recognize it as hyperactive and impulsive.
- Fidgets or taps hands or feet.
- Difficulty staying seated for prolonged periods.
- Climbs or runs in situations where it is inappropriate. (However, it is limited in adolescents and adults.)
- Unable to engage in activities or play quietly.
- Restless being still for an extended time, as in restaurants, meetings.
- They talk excessively.
- Speaks an answer before a question has been completed.
- Difficulty waiting for a turn.
- They tend to interrupt others in between conversations.
ADHD Combined Type
ADHD either includes inattentiveness or hyperactive-impulsiveness. When a person has 6 or more symptoms of each type, they have combined type.
Some techniques to help people with combined type ADHD includes:
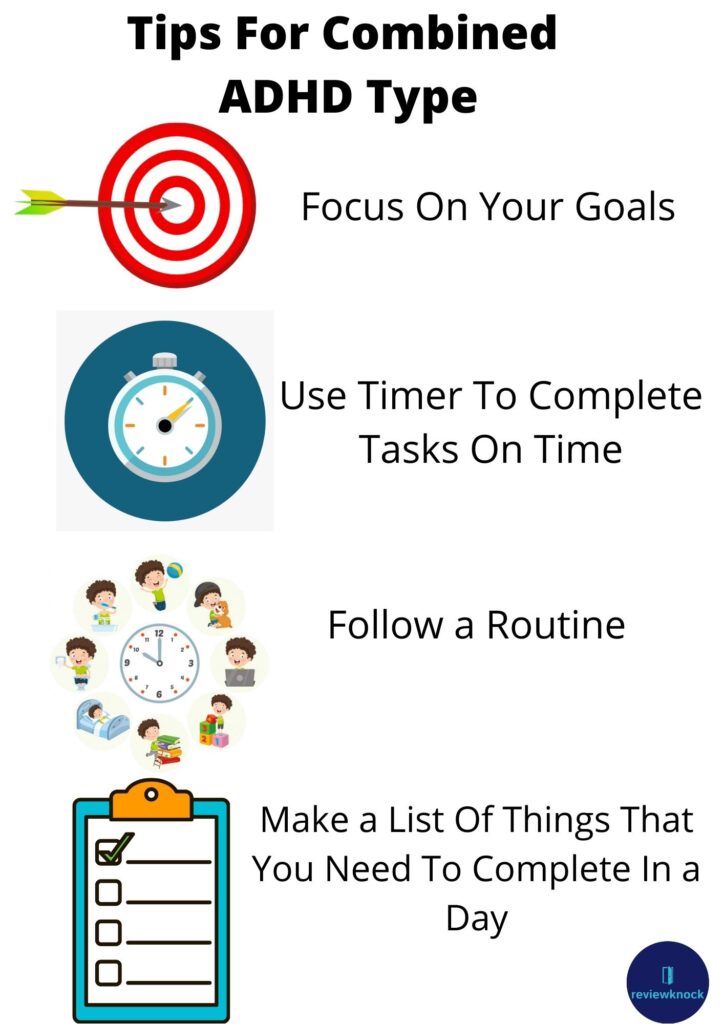
For children–
- Develop a routine.
- Be consistent with rules.
- Reward good behavior.
- Minimize distractions.
For adults–
- Try to use reminders.
- Break down tasks into smaller steps.
- Create and use lists to remember things.
- Maintain a routine.
ADHD Brain
The deficits in the ADHD brain do not affect one’s intelligence levels but reduce the capability of a person to manage emotions and regulate attention.
The hippocampus and amygdala are small in the brain that is responsible for regulating emotional behavior. Several studies have reported that such people have smaller brain volumes in sub-cortical areas. Also, their brain matures at a slower pace.
Also, dopamine levels are decreased in the brain. Different stimulant medications can help to treat it by boosting dopamine production.
Brain function can not be diagnosed by brain scanning. But there are different ways to do it, like :
• Detailed interview with the patient
• Checking school reports and medical history
• Distinct tests to measure distractability and memory.
ADHD Causes
- Genetic Factors– The risk of ADHD has been more prevalent in first-degree relatives such as parents and siblings. According to a study among 457 relatives of children, the risk of ADD and antisocial behavior was higher than among normal controls. The child has a 1 in 4 chance of having a parent with the same disorder.
- Biological– It can occur because of the interplay of certain neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine and dopamine. When the working mechanism of these chemicals changes in the brain, they cause instability in the brain’s attentional networks.
- Environmental Factors– Adverse home environment may contribute to inattentiveness and hyperactivity in children. Among all environmental factors, nicotine exposure and maternal smoking are more prevalent. Other factors include maternal anemia, low birth weight, prematurity, and childhood diseases such as thyroid, anemia, and metabolic disorders.
- Head Injury– Hyperactivity is directly correlated with the head injury in a study conducted on 95 children of 5-15 years. The development of visual skills is also interrupted even by a mild degree of head injury.
- Food Allergy– It is one of the possible causes of this disorder. Food items such as chocolate, egg, citrus, and cheese may trigger hyperactive behavior in patients. A hypoallergenic diet is occasionally used on such patients, but it needs further study to decide its effectiveness.
People who are at more risk
Those who were born prematurely. Individuals who suffered from a brain injury; in the womb or after a severe head injury later in life.
ADHD in Children
ADHD is a neurological disorder that appears in the early years, usually before seven, and often persists in adulthood. It is one of the commonly diagnosed mental disorders in children.
They suffer from concentration difficulties, relationship troubles with others, and poor performance in school. Besides, they may also have low self-concept and poor self-esteem.
Also, they can face difficulty in recognizing the needs and desires of other people. Some of the symptoms are more prevalent in boys as compared to girls.
REPORTS ON ADHD
It affects about 11% of children between the age of 4 and 17. About 13% of men are victims of this disorder, while ADHD in women is about 4.2%. Also, boys are more than twice likely to be affected by it as compared to girls.
According to DSM surveys, the disorder occurs in most countries in about 2.5% of adults and 5% of children.
Symptoms of ADHD in boys include
- Hyperactive behavior
- They face a difficult time managing their emotions. It can take a toll on their self-esteem.
- Distractible
- Excessively talkative
- Little or no sense of danger
- Being unable to wait for their turn
ADHD symptoms in girls include
- Talking all the time.
- Frequent crying.
- Interrupting conversations.
- Trouble paying attention
- Appears withdrawn
- Daydreaming
- Easily distractible
According to DSM, population surveys suggest that ADHD disorder occurs in most cultures in about 2.5% of adults and 5% of children.
Adult ADHD Symptoms
Symptoms of adult ADHD also have gender differences. Research has shown that men usually show externalized signs like impulsivity and hyperactivity.
In contrast, symptoms of ADHD in women are typically internalizing, like inattentiveness and low self-esteem.
ADHD fatigue is another common symptom experienced by people. It can be because of different factors like hyperactivity, poor sleep, and side effects of medication.
The adults face deficits in executive functions that affect their ability to start and sustain attention on a task. This adult paralysis can lead to avoidance and procrastination, which will affect their productivity results.
It can also lead to negative statements by others who might get annoyed and confused by this inconsistent pattern of work performance.
ADHD boredom intolerance is also prevalent in both children and adults. All this will eventually decrease one’s motivation levels and they might not be excited and hopeful about something again.
There are several coping strategies for the same that includes:
• Set smaller goals.
• Break down tasks into smaller chunks.
• Practice rewarding yourself for every little step you take to reach your goals.
• Incorporate physical activity in daily routine.
“Try to find one piece of progress that gives you the needed strength and motivation to keep trying.”
Do you feel it is hard to make a decision? It is because the adults also have analysis paralysis. But, I have enlisted some of the strategies that you can follow to make better and timely decisions. These include:
- Limit your choices to avoid information overload.
- Listen to your intuition.
- Find a quiet place to think.
- Try to consider the pros and cons associated with a specific decision.
- Spend more time on essential things.
- Feel good about your decision.
Some Common Symptoms In Adults Include:
- Hyperactivity
- Fidgeting
- Impulsivity
- Irritability
- Risk-taking behaviors
- Forgetfulness
- Lack of concentration
- Short attention span
- Anxiety
- Excitement
- Mood swings
- Learning disability
- Sleep deprivation
What Will Happen If You Don’t Treat ADHD On Time?
Untreated ADHD in adults can trouble one throughout life. These individuals will face difficulty in sustaining their attention for long periods and can be hyperactive and restless.
Moreover, it can also lead to emotional problems like depression, low self-esteem, and anxiety, leading to job instability. Also, this will affect one’s relationships, such as negative child-parent relationships.
According to a 2016 study, spouses of these individuals may feel more neglected than those having partners without any ADHD symptoms.
One study also suggested that these adults may be unable to stay focused at their work. It could lead to difficulty in staying at the same job for a long time.
ADHD Diagnosis
To be diagnosed with this disorder, the individual must have at least six symptoms of inattentiveness or six symptoms of impulsivity and hyperactivity.
Standard ADHD tests used in diagnosis include ADHD rating scales that can identify signs which can reveal how a person functions at home, school, and work environment.
Standardized questionnaires filled up by parents, school teachers, and professionals are made use of in diagnosis. A neurological examination can also provide additional information.
Diagnosis can be pretty tricky because there is no specific ADHD test, such as taking a blood sample or conducting an X-ray.
Also, other problems can cause similar behavior, such as language and hearing difficulties or dyslexia.
The kind of symptoms professionals look for diagnosing it includes:
- The typical symptoms include persistent inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsive behavior in abnormal frequency and severity.
- These symptoms should be present before the age of 7 years.
- It should be visible in at least two settings; home, school or workplace, etc.
- They are sufficient to impair social, academic, and occupational functions.
ADHD Assessment
ADHD assessment is a multi-step approach that involves a rating scale, clinical examination, behavioral observations, interviews, and ADHD questionnaires.
A variety of rating scales have been in practice to assess individuals’ psycho-social functioning and behavior in general. Teachers or individuals themselves can complete these.
Some standard ADHD rating scales for children include:
- Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL)- For ages 6 to 18.
- Connors- Well’s Adolescent Self-Report Scale- For teenagers
- National Institute for Children’s Health Quality (NICHQ) Vanderbilt Assessment Scale- For age 6 to 12
- Connors Comprehensive Behavior Rating Scale (CBRS)- For ages 6 to 18
ADHD test for adults:
- Adult ADHD Self- Report Scale
- Adult ADHD Clinical Diagnostic Scale
- ADHD Rating Scale-IV
- Brown- Attention Deficit Disorder Assessment Scale (BADDS) for Adults
Observation serves as an essential tool to identify the specific symptoms. Reports from teachers or family members can help provide information about the problems related to behavior or social functioning in children and adolescents.
Clinical examination for it involves inspections of psychiatric difficulties or vision or hearing impairments, and neurological immaturity.
ADHD Treatment
The common medications used in the treatment include:
- Stimulants– It has been used for several decades to treat ADHD disorder. These might help focus your attention and ignore distractions from external stimuli. Stimulants are successfully used for about 70%- 80% of people. Some are for children over age three and some for over age 6. The two common stimulants for ADHD include methylphenidate and amphetamine.
- Non- Stimulants– For cases where stimulants don’t work, these can improve symptoms of lack of concentration and impulsivity.
- Anti-Depressants– ADHD adults and children may have depression, anxiety, or other mood disorders. They can take anti-depressant along with stimulants.
NOTE: You should take these medicines only after consulting the doctor and discussing the risks and benefits of these drugs with them. These are entirely safe when appropriately monitored by a professional.
ADHD Treatment Without Medication
Some of the proven natural remedies and alternative ADHD treatment for adults include:
• Include omega-3 fatty acid sources such as fish oil in your diet. It is beneficial for proper brain and nerve cell function. As the body of individuals with this disorder is not able to make omega-3 by itself.
• Some of the essential vitamins and minerals to be included in the diet are
- Vitamin C – works as a building block of neurotransmitter
- Zinc – regulates levels of dopamine in the brain.
- Iron and B6- increases dopamine
• Exercise regularly– Engage in short-term, aerobic exercise (yoga) to help deal with the symptoms like inattentiveness.
• Practice mindfulness meditation– This can help develop positive emotions, manage stress, and increase self-awareness. Studies have shown the efficiency of mindfulness to support the treatment of ADHD.
• Engage in behavior therapy and cognitive behavior therapy. These have been used on a large scale to eliminate destructive behaviors and thoughts by cognitive restructuring.
Natural Supplements For ADHD Child
Omega 3
Zinc
Iron
Magnesium
Vitamin-C
Other natural ways to treat ADHD:
• Indulge in some daily physical exercise.
• Eat a healthy diet.
• Drink plenty of water. Stay hydrated.
• Take an adequate amount of sleep.
ADHD Child Activities

- Team Sports– It helps develop social skills and provides opportunities for physical activity.
- Art Techniques– It is an excellent option for ADHD children to help them sit in one place and learn to pay attention in school.
- Outdoor Activities– Walking for at least 20 minutes, fishing, hiking, or gardening.
- Martial Arts– Helps to engage in physical activity and channel energy in something productive.
- Music Exercises– These can be an effective tool to provide calmness to the brain of the child, and it also boosts dopamine levels.
Behavior Therapy For ADHD
It can help eliminate negative behaviors and replace them with positive ones. Behavior therapy can help learn skills that control the symptoms.
Some people have found it to be a valuable strategy to manage their symptoms without medications. However, some use the therapy along with the medicines.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), behavioral therapy and CBT help reduce symptoms in ADHD children.
Behavior Therapy For Children
The plan requires the entire family to set goals and eliminate the child’s negative behaviors. The therapy sessions will give both children and parents the tactics they need to make changes successfully.
Some of the skills children will be able to learn includes:
- Paying attention in class
- Completing work on time
- Keeping things in an organized manner
- Completing daily chores
Behavior Therapy For Adults
ADHD adults face distinct challenges and need different strategies to tackle the symptoms.
If you’re an adult with ADHD, this can help you overcome your negative thoughts by reframing them. It will support you to look at your past struggles and how you could have managed the situation in a better way.
Some of the significant benefits are:
- Stress reduction
- Eliminating negative emotions
- Figuring out behavior patterns
- Changing self-defeating behaviors
- Making time for self-care
Benefits of ADHD
- The ADHD mind is unique. Some individuals are creative and inventive thinkers.
- They may be willing to try out new things and take risks.
- Some individuals might be hyper-focused, leading them to avoid any outside distractions and continue working on a task until it gets completed.
- Also, they are more energetic than other people. So, they can channel that endless energy to achieve success in school or at work.
- It may give individuals a distinct perspective towards life and support them to approach situations with a thoughtful eye.
ADD Vs. ADHD
Are ADHD and ADD the same thing? Let’s find out.
Many people believe that ADD and ADHD are the same things. But these are entirely different terms. The former was used to describe the inattentive type and is not a medical diagnosis at present.
However, the latter is a neurological disorder. The difference between them is that people with ADD often lack symptoms of hyperactivity. It is best described as ADHD without hyperactivity.
Most visible signs of ADD
- Inattentiveness
- Distractability
- Poor working memory
- Ineffective executive functions
ADHD Vs. Autism
Are ADHD and autism-related?
Both of these conditions are neurological disorders with some common symptoms, but they are entirely different. Some of the critical differences between them include:
Attention Span
ADHD children may not be able to pay attention to any subject. But an autistic child can focus on things they love doing but may not focus on things that seem less attractive to them.
Social Difficulties
Autistic children find it hard to express themselves verbally, don’t use gestures while communicating, and struggles to make eye contact.
However, those with ADHD talk continuously and interrupt others in between conversations.
Repeated Tasks
The autistic child likes order and repetition and may get upset with a new routine. However, an ADHD child gets bored with the same tasks and does not like to work for a longer duration.
ADHD Vs. OCD
Some of the symptoms of both these disorders overlap, making it difficult to differentiate between them. Some of the differences in their symptoms are:
• ADHD is caused by under-activity in the brain ( low dopamine levels), whereas OCD is because of over-activity ( high serotonin levels).
• The former is an externalizing disorder that is because of difficulties in interacting with the environment. However, OCD is an internalizing disorder related to stress, obsessive thoughts, and compulsive behavior.
• OCD people tend to avoid risks and uncertainty that are absent in the former.
• These people find it difficult to pay close attention to details. However, those with OCD feel the need to follow a strict routine and carry out tasks consistently.
Conclusion
ADHD can affect your life on a large scale, be it in school, work, or your relationships. It usually takes place during the early years.
But, many people with this disorder are living their life successfully by following some basic management strategies. You can ‘grow out of it; however, you can manage its symptoms.
You can follow some of the natural remedies that I have mentioned above.
If you or your child has ADHD, then you should consult a professional. They can help manage your symptoms and maximize your opportunities.
Have you tried any of the tips that I mentioned above? Also, if you have any queries you can contact me personally too!
